Abstract: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive motor neuron loss, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis, and ultimately, death. While current treatments aim to manage symptoms and slow disease progression, they fall short of offering remission, reversal, or cure. This paper explores the definitions and probabilities of these concepts in the context of ALS, examines the potential benefits of cannabinoid therapy in managing symptoms and impacting disease progression, and highlights the need for further research in this critical area.
1. Introduction
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a fatal neurodegenerative disease affecting motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. The progressive degeneration of these neurons leads to muscle weakness, atrophy, difficulty speaking, swallowing, and breathing, ultimately resulting in paralysis and death, typically within 2-5 years of diagnosis. Currently, there is no cure for ALS, and existing treatments focus primarily on symptom management and slowing disease progression. This paper aims to clarify the definitions of remission, reversal, and cure in the context of ALS, and to explore the potential of cannabinoid therapy as a therapeutic approach.
2. Defining Remission, Reversal, and Cure in ALS
The terms remission, reversal, and cure are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings, especially in the context of chronic and progressive diseases like ALS.
- Remission: In the context of ALS, remission would imply a significant reduction in the severity of the disease's symptoms and a halt to the progression of motor neuron degeneration. Essentially, the patient would experience a period of stability where their functional abilities are maintained and do not worsen. This doesn't necessarily mean the underlying disease process is eradicated, but rather that its clinical manifestations are significantly suppressed.
- Reversal: Reversal in ALS would suggest a recovery of lost motor neuron function and a restoration of muscle strength and function. This would imply that the underlying pathological processes responsible for motor neuron degeneration are not only halted but also reversed, leading to functional improvements.
- Cure: A cure for ALS would mean the complete eradication of the disease, including the underlying pathological mechanisms. This would involve eliminating the source of motor neuron degeneration, preventing further neuronal loss, and ideally, restoring lost function.
3. Probability of Remission, Reversal, and Cure in ALS
Currently, the probability of a spontaneous or treatment-induced remission, reversal, or cure for ALS is extremely low. While research is ongoing and new therapies are being developed, no treatment has been shown to consistently and reliably induce any of these outcomes.
- Remission: While anecdotal reports of individuals experiencing periods of stability or slowed progression exist, these are rare and often difficult to definitively attribute to specific treatments. The heterogeneity of ALS and the unpredictable nature of its progression make it challenging to determine true remission versus natural fluctuations in the disease course.
- Reversal: To date, there is no evidence to suggest that any existing treatments can reverse the damage caused by motor neuron degeneration in ALS.
- Cure: A cure for ALS remains an aspirational goal. Despite significant advances in understanding the genetic and molecular underpinnings of the disease, the complex and multifactorial etiology of ALS has made it challenging to develop curative therapies.
It's crucial to emphasize that ongoing research efforts are focused on identifying potential therapeutic targets and developing new strategies that may eventually lead to disease-modifying or even curative treatments.
4. Cannabinoid Therapy in ALS: Potential Benefits
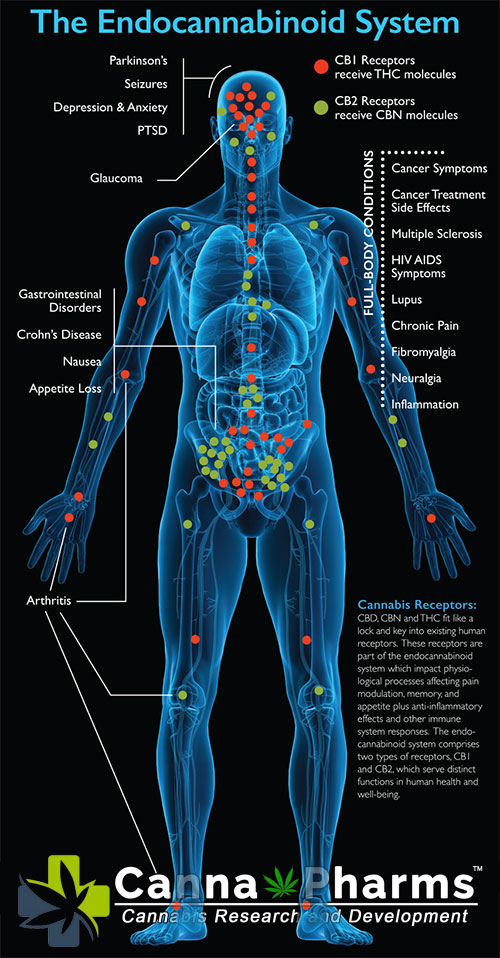
Cannabinoids, the active compounds found in cannabis, have gained increasing attention for their potential therapeutic benefits in various neurological disorders, including ALS. While research is still in its early stages, several potential mechanisms suggest that cannabinoids may offer benefits in managing ALS symptoms and, potentially, impacting disease progression.
4.1. Potential Mechanisms of Action:
- Neuroprotection: Some studies suggest that cannabinoids, particularly cannabidiol (CBD), may have neuroprotective properties, potentially protecting motor neurons from damage and slowing the rate of degeneration. CBD has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which may contribute to its neuroprotective potential.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Inflammation plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of ALS. Cannabinoids, particularly CBD, have demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory properties, potentially mitigating the inflammatory cascade that contributes to motor neuron damage.
- Muscle Relaxation and Spasticity Reduction: ALS often leads to muscle spasticity and cramps, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. Cannabinoids, particularly tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have well-documented muscle relaxant properties that can help alleviate spasticity and improve muscle relaxation.
- Pain Management: Pain is a common symptom in ALS, arising from muscle cramps, spasticity, and nerve damage. Cannabinoids can interact with pain pathways in the central nervous system, providing pain relief and improving comfort.
- Appetite Stimulation and Nausea Reduction: ALS can lead to difficulties with swallowing and reduced appetite, leading to weight loss and malnutrition. THC can stimulate appetite and reduce nausea, helping patients maintain a healthy weight and improve their nutritional status.
- Sleep Improvement: Sleep disturbances are common in ALS, driven by pain, spasticity, anxiety, and breathing difficulties. Cannabinoids can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, helping patients improve their overall well-being.
4.2. Benefits of Cannabinoid Therapy in ALS:
Based on the proposed mechanisms of action, cannabinoid therapy may offer the following benefits for ALS patients:
- Symptom Management: Cannabinoids can effectively manage various symptoms associated with ALS, including pain, spasticity, muscle cramps, insomnia, and appetite loss, improving patients' quality of life.
- Potential Disease Modification: While more research is needed, some preclinical studies suggest that cannabinoids may have the potential to slow down the progression of ALS by protecting motor neurons and reducing inflammation.
4.3. Considerations and Challenges:
Despite the potential benefits, several considerations and challenges need to be addressed regarding cannabinoid therapy for ALS:
- Limited Clinical Evidence: The number of clinical trials examining the efficacy and safety of cannabinoids in ALS is still limited. More robust and well-designed clinical studies are needed to confirm the benefits and determine the optimal dosage and formulations of cannabinoids for ALS patients.
- Side Effects: Cannabinoids can cause side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. The potential side effects need to be carefully weighed against the potential benefits, and patients should be closely monitored for adverse effects.
- Drug Interactions: Cannabinoids can interact with other medications, potentially altering their effects. It's essential to carefully assess potential drug interactions before initiating cannabinoid therapy.
- Legal and Regulatory Issues: The legal status of medical cannabis varies widely across different jurisdictions. Patients need to be aware of the legal regulations in their area before using cannabinoid therapy.
- Variability in Product Quality: The quality and composition of cannabis products can vary widely, potentially affecting their efficacy and safety. Patients should obtain cannabis products from reputable sources and ensure that they are properly labeled and tested for purity and potency.
- Specific Cannabinoid Ratios: More research needs to determine the optimal ratios of cannabinoids for treating ALS as different ratios may address different symptoms.
5. Conclusion
While remission, reversal, and cure remain elusive goals in ALS, ongoing research is crucial for developing effective treatments that can significantly improve the lives of those affected by this devastating disease. Cannabinoid therapy holds promise as a potential adjunctive treatment for managing symptoms and, possibly, influencing disease progression in ALS. However, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to fully evaluate the efficacy and safety of cannabinoids in ALS. In the meantime, patients with ALS should discuss the potential benefits and risks of cannabinoid therapy with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions about their treatment plan, alongside current standard of care therapies. Further research into the endocannabinoid system and its role in neurodegeneration is crucial to unlock the full therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in ALS and other neurological disorders. This research must consider specific cannabinoid ratios, product formulations, and individualized patient needs to maximize benefits and minimize potential risks.